Understanding the Federal Reserve Balance Sheet
The Federal Reserve System is the central bank of the United States and is responsible for the nation's monetary policy. The Fed's primary goals are to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and manage long-term interest rates. The Fed also helps to create stability in the financial system, especially during times of recession—or negative economic growth—and financial instability.
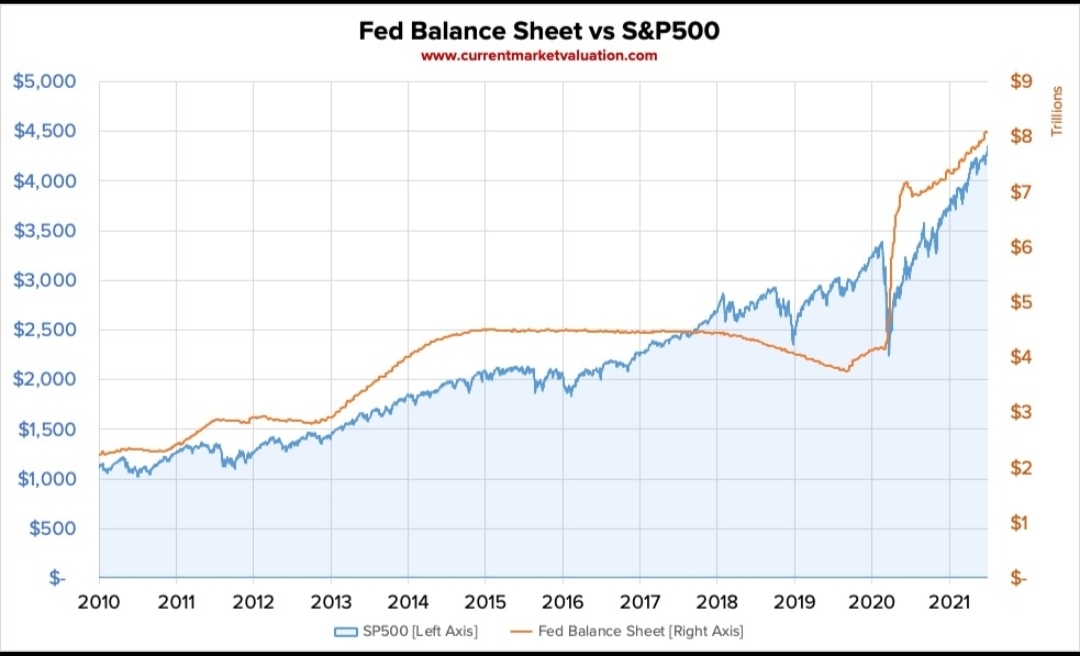
For decades, the Fed watchers have relied on movements in assets or liabilities of the Fed to predict changes in economic cycles. The financial crisis of 2007-08 not only made the Fed's balance sheet more complex, but it also aroused the interest of the general public.4 Before going into the details, it would be better to take a look at the Fed's assets first and then its liabilities.
Like any business organization, the Federal Reserve maintains a balance sheet listing its assets and liabilities.
The Fed's assets include various Treasuries and mortgage-backed securities purchased in the open market and loans made to banks.
Liabilities for the Fed include currency in circulation and bank reserves held at commercial banks.
During economic crises, the Fed can expand its balance sheet by buying more assets, such as bonds—called quantitative easing (QE).
Read More: https://www.investopedia.com/articles/economics/10/understanding-the-fed-balance-sheet.asp#toc-the-bottom-line
精彩评论